Back
Contents
Perpetual Futures. What They Are and How They Work?


Demetris Makrides
Senior Business Development Manager

Vitaly Makarenko
Chief Commercial Officer
A perpetual future contract doesn’t include the expiration date unlike traditional futures contracts. Traders are able to hold a position as long as they want. Furthermore, perpetual future contracts are traded at a price that is equal or close to the spot market price.
Key takeaways:
- What is a perpetual futures contract?
- What are the differences between perpetual and traditional futures?
- Pros and cons of perpetual futures.
- How to trade perpetual futures properly?
- What is better, perpetual futures or spot trading?
The Definition of Perpetual Contracts
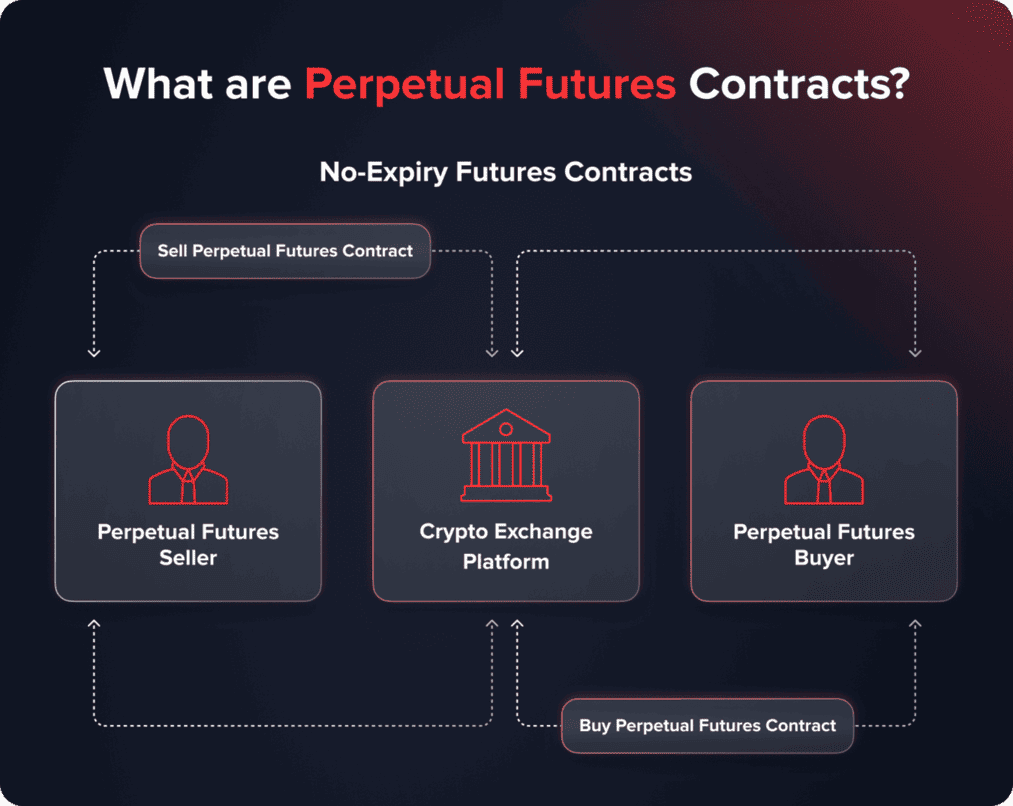
Under the term ‘perpetual futures contract’ the financial world understands derivative trading instruments that have no expiration date; which is why holders of such contracts are able to speculate on prices indefinitely.
The first reference to such a type of a futures contract appeared in 1993 in a paper written by Robert Shiller. Meanwhile, the instrument came into existence much later, in 2016. BitMEX was the first trading platform that enabled its clients to buy and sell perpetuals for Bitcoin.
At present, perpetual futures contracts mainly refer to crypto trading, but this instrument can also include other underlying assets like indices or commodities.
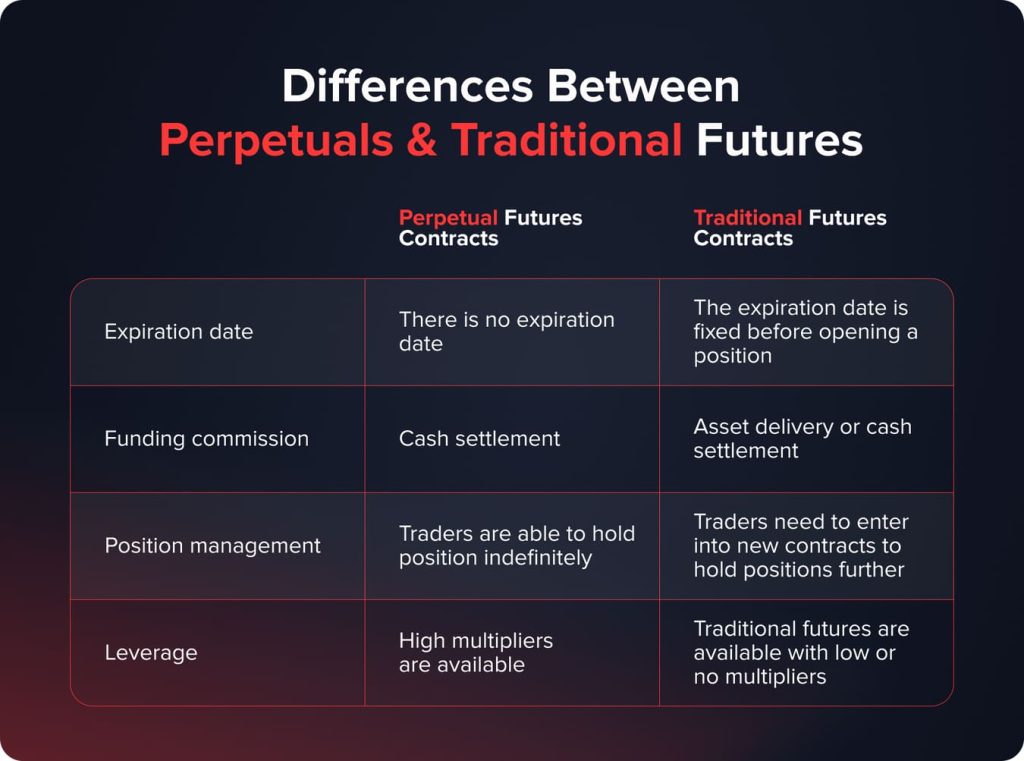
Perpetual Futures Vs Traditional Futures. What are the Main Differences?
Let’s dive deeper into the differences between perpetuals and traditional futures.
To understand the above-mentioned differences better, we need to dwell on every criterion in detail.
Expiration Date
That is the main difference between perpetuals and traditional contracts. When you buy or sell a traditional futures contract, the expiration date is predetermined (14 days, 30 days, 180 days, etc.). As for perpetual contracts, you may hold your position without any limits, as long as you want.
Funding commission
Funding is the next difference between the two futures contract types. The prices of the underlying assets of traditional futures automatically match the spot prices as the expiration date comes closer. Perpetual contracts do not include such a mechanism; which is why funding serves as a balancer.
Under the funding commission (funding rate) traders understand periodic payments between the holders of long and short positions. The instrument motivates the less popular side to keep a balance between the prices of perpetuals and spot prices.
When the funding rate is positive, the contract’s price is getting higher than the spot price. In such a situation, holders of long positions have to pay the funding rate in favor of the shorts. The negative funding commission means that the contract’s price is lower than the spot one, and the shorts pay in favor of the longs.
You may also like

Note! The funding rate is not fixed and depends on the difference between a contract’s price and the spot one. There are some moments when it is not recommended to open positions due to exceptionally high funding rates.
Let’s check how the funding commission on a perpetual contract works in practice.
- Binance usually charges 0.01% funding commission when the market doesn’t experience sharp price movements.
- A trader opens a long perpetual contract with the overall volume of 100 USDT (approximately $100) using the leverage 1:10 (10x). The margin is 10 USDT ($10).
- The positive commission means that he needs to pay funding in favor of the shorts. The commission is charged three times a day. Furthermore, the commission rate is multiplied by the chosen leverage. 0.01% becomes 0.1% (0.01 * 10).
- As such, a holder of a long perpetual contract pays a $0.01 funding commission three times a day.
Position management
Holders of perpetual contracts are able to keep their long/short positions for as long as they want. Traditional futures contracts have a predetermined expiration date and holders cannot somehow affect it. The only option lies in closing one position and opening another futures position with a longer expiration.
Leverage
Perpetuals are available with much higher multipliers than traditional futures contracts. Top-rated exchanges enable their traders to use leverages up to 1:125. On the one hand, such multipliers open brand new opportunities for traders. On the other hand, using high leverages implies higher risks as well.

Pros and Cons of Perpetual Futures
The popularity of perpetual futures contracts is gaining momentum. According to the Block, the overall volume of the crypto perpetuals market exceeds $200 billion. Here are the main advantages of perpetual contracts:

- Perpetuals are not limited by the expiration date. The core feature of such a contract type is its main advantage as well. Traders are able to hold their positions as long as they want; which is why traders can easily adjust their strategies to market changes.
- Perpetual futures contracts are characterized by the highest liquidity. In many cases the liquidity of perpetuals is even higher than on the spot market. Traders may get the best possible price when buying and selling perpetuals.
- Such an instrument is available with higher multipliers; therefore, traders may open positions for higher capitals investing small sums. For instance, the leverage 1:100 (100x) makes it possible to invest just $10 and open a position for $1,000.
When taking into account advantages only, perpetual contracts seem to become a perfect instrument for a trader. Meanwhile, there are some pitfalls as well. What are the key weak points of this trading instrument?
- High multipliers provide traders with better opportunities as they can open positions for large amounts investing less capital. At the same time, leverage increases the risks taken significantly, especially in the crypto market. When using the multiplier 1:100, the 1% move of an asset’s price in the opposite direction leads to a position liquidation. Beginner traders are not recommended to apply multipliers higher than 1:10.
- Funding rates can be exceptionally high depending on certain market conditions. During ‘calm’ periods, funding rates do not affect your capital significantly, but sharp price movements that happen rather frequently can eat up to 1-2% of your position three times a day. As such, holding a perpetual may be unprofitable.
Hence, perpetual futures contracts have both advantages and weak points. Such an instrument is rather attractive for traders, especially in the crypto market. However, before trading perpetuals you need to understand the risks and avoid or minimize them.
What is Perpetual Futures Trading? The Top Strategies
When using perpetuals traders need to understand which strategies to apply. Here is the list of the most widespread trading ‘approaches’ for perpetual futures trading:
Speculation
This trading strategy is as simple as opening a door. Traders utilize diverse technical or fundamental analysis instruments to understand the direction in which an asset’s price is going to move further. Based on that understanding, a trader opens either a long or a short position. Speculation is effective for both short-term and long-term trading styles.
Trend Following
The strategy is effective for short-term trading styles (scalping, intraday trading). Utilizing technical instruments traders need to identify the current market trend and how strong it is. Then they open long and short positions accordingly. Furthermore, a strong trend enables traders to use high multipliers to increase possible profits.
Hedging
Perpetuals are widely used as hedging instruments. Traders open one position in the spot market, and then hedge it with a perpetual in the opposite direction. For instance, a trader holds Ethereum in the spot market and opens a short perpetual contract to hedge his position.
You may also like

Arbitrage
Traders may use the price difference between the spot market and perpetuals to get profits. Such a strategy implies simultaneous buying an asset in one market and selling the same asset in another market. For instance, you have found the price difference for Bitcoin. Buy BTC in the spot market and sell in the market of perpetual contracts or vice versa.
Funding Arbitrage
The strategy means that a trader needs to detect the difference between funding rates on two trading platforms. For instance, one crypto exchange offers 0.05% for Bitcoin perpetual contracts while another exchange gives 0.01% for the same instrument. Traders open two contracts, long and short, to get profits from the difference. Meanwhile, you need to take into account fees for buying/selling contracts.
Perpetual Futures Vs Spot. What is Better?
What is the main advantage of perpetual futures? As we have already mentioned, they do not have expiration dates. Meanwhile, in the spot market traders may hold their positions as long as they want as well. What are the main differences between the spot market and perpetuals, and which instrument is better?
Perpetuals Vs Spot. The pros of perpetual futures:
- Perpetual contracts are available with multipliers. Some exchanges offer leverage up to 1:125; which is why traders may use less capital to get higher profits.
- Perpetuals are widely used in different strategies like hedging and arbitrage.
- Perpetual futures contracts match all trading styles (both short-term and long-term ones).
Perpetuals Vs Spot. The pros of spot positions:
- Traders do not pay funding commissions; therefore, sharp market movements do not affect them.
- There is no risk of liquidation that appears when a trader uses leverage.
Hence, it is hard to answer which instrument is better. Both perpetual contracts and spot positions have their own strong points, and traders use them in different ways.
The Bottom Line
Perpetual futures contracts provide traders with a possibility to speculate on the future asset prices being not limited by the expiration date. Furthermore, perpetuals enable traders to use leverage and get higher profits with less capital invested.
When compared to the spot market and traditional futures, this instrument has both advantages and weak points. Traders widely use perpetuals in speculation, hedging, trend following, and arbitrage strategies.
FAQ
Such a trading instrument is widely used in different strategies and has no expiration date; which is why traders may hold their positions indefinitely.
Funding is the commission paid by the longs or shorts that helps keep balance between a perpetual contract price and an underlying asset’s price in the spot market.
Professional traders use perpetuals for trend following, hedging, speculation, and different types of arbitrage.
Updated:
December 19, 2024